Hydrogen gas
Hydrogen gas (H2) is a colorless, odorless, tasteless, non-toxic, and highly combustible gas. It is the lightest element in the universe, and it is the most abundant chemical substance in the universe, constituting roughly 75% of all normal matter. Stars such as the Sun are mainly composed of this gas in the plasma state. Most of the H2 on Earth exists in molecular forms such as water and organic compounds.
Sepher gas kavian is a producer and importer of high quality laboratory gases and gas mixtures (calibration gases) and all related equipment for various industries. Sepher gas kavian is active in supplying pure laboratory gases and mixed gases in percentage, ppm, ppb such as hydrogen gas.
This gas with purity percentage of 99.999, 99.9995, 99.9999 is available in carbon steel cylinders.
Hydrogen gas grade 99.999 is available in 5 and 10 liter cylinders with a pressure of 70 bar and in 50 liter cylinders with a pressure of 150-140 bar.
99.999 grade this gas (JC grade) for gas chromatography is available in 5 and 10 liter cylinders with a pressure of 70 bar and in 50 liter cylinders with a pressure of 150-140 bar.
Imported this gas grade 99.999 is available in 50 liter cylinders with a pressure of 140-150 bar.
Imported Hydrogen gas grade 99.9995 is available in 50 liter cylinders with a pressure of 140-150 bar.
Imported H2 gas grade 99.9999 is available in 50 liter cylinders with a pressure of 140-150 bar.

Resources
This gas can be produced from a variety of resources, including:
Fossil fuels: H2 can be produced from fossil fuels, such as natural gas, by a process called steam reforming. This process involves reacting steam with methane at high temperatures and pressures to produce hydrogen and carbon monoxide.
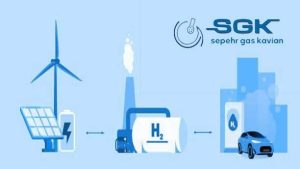
Water: Hydrogen gas can be produced from water by a process called electrolysis. This process involves passing an electric current through water to split it into hydrogen and oxygen.
Biomass: This gas can be produced from biomass, such as wood, by a process called gasification. This process involves converting biomass into a gas that can then be used to produce H2.
Solar energy: This gas can be produced from solar energy by a process called photolysis. This process involves using sunlight to split water into hydrogen and oxygen.
The most common method for producing this gas is steam reforming of natural gas. This process is relatively inexpensive and efficient, but it produces carbon dioxide emissions. Electrolysis of water is a more expensive process, but it produces no emissions. Photolysis of water is the most expensive process, but it is also the cleanest.
The choice of which method to use for producing this gas depends on a number of factors, including the cost, the environmental impact, and the availability of resources.
Produce
There are four main methods for producing this gas:
Steam reforming of natural gas
Electrolysis of water
Gasification of biomass
Photolysis of water
Steam reforming of natural gas is the most common method for producing H2. It is a relatively inexpensive and efficient process, but it produces carbon dioxide emissions. In this process, steam is reacted with methane at high temperatures and pressures to produce this gas and carbon monoxide.
Electrolysis of water is a process that uses electricity to split water into H2 and oxygen. This process is more expensive than steam reforming, but it produces no emissions. In this process, an electric current is passed through water, which causes the water molecules to split into H2 and oxygen.
Gasification of biomass is a process that converts biomass into a gas that can then be used to produce hydrogen. This process is clean and renewable, but it can be expensive to process the biomass. In this process, biomass is heated in the presence of oxygen or steam to produce a gas that contains this gas, carbon monoxide, and other gases.
Photolysis of water is a process that uses sunlight to split water into this gas and oxygen. This process is the cleanest method for producing this gas , but it is also the most expensive. In this process, sunlight is used to excite electrons in water molecules, which causes the water molecules to split into hydrogen and oxygen.
The choice of which method to use for producing this gas depends on a number of factors, including the cost, the environmental impact, and the availability of resources.

Technical specification
| Chemical formula | H2 |
| Molecular Weight | 2.016 g/mol |
| Color and smell | It is colorless and odorless |
| Density | About 0.00897 g/cm³. |
| Melting point | -25.1 degrees Celsius |
| Boiling point | -254.3 degrees Celsius |
| Flammability |
It has high flammability |
Application
This gas is a versatile gas with a wide range of applications. Here are some of the most common uses of this gas:
Fuel cells: This gas fuel cells are devices that convert H2 and oxygen into electricity and water. They are used in a variety of applications, including cars, buses, forklifts, and backup power systems.
Petroleum refining: This gas is used in the refining of petroleum to remove sulfur and other impurities. This makes the petroleum cleaner and more environmentally friendly.
Fertilizer production: This gas is used to produce ammonia, which is a key ingredient in fertilizer. Ammonia is used to increase crop yields and improve soil quality.
Metalworking: This gas is used in metalworking to reduce the risk of fire and explosion. It is also used to heat and treat metals, and to weld and braze them.
Chemical manufacturing: This gas is used in the production of a wide variety of chemicals, including methanol, ammonia, and hydrochloric acid.
Energy storage: This gas can be used to store energy from renewable sources, such as solar and wind power. This allows the energy to be used when it is needed, even if the sun is not shining or the wind is not blowing seper gas kavian
Danger
Here are some of the dangers of this gas:
Fire and explosion: This gas is highly flammable and can form explosive mixtures with air. If a hydrogen leak occurs, it is important to evacuate the area and call the fire department immediately.
Asphyxiation: This gas is lighter than air, so it can rise rapidly and displace oxygen. If a H2 leak occurs in an enclosed space, it is possible for the oxygen level to drop to a level that is not enough to support life. This can lead to asphyxiation, which is a condition in which the body does not get enough oxygen.
Breathing difficulty: This gas can also cause breathing difficulty in people with asthma or other respiratory problems. If you have a respiratory problem, it is important to avoid breathing hydrogen gas.
Skin and eye irritation: This gas can irritate the skin and eyes. If you come into contact with H2, it is important to wash the affected area with soap and water and to seek medical attention if the irritation is severe.