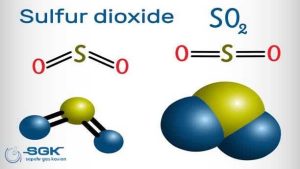
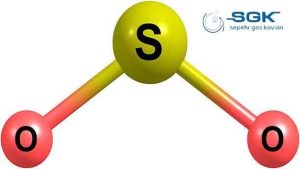
Sulfur dioxide gas
Sulfur dioxide (SO2) is a colorless gas with a strong, pungent odor. It is a major air pollutant that is produced by the burning of fossil fuels, such as coal and oil, and by the smelting of metal ores. SO2 is also released naturally from volcanic eruptions.
Sepher gas kavian company is a producer and importer of high quality laboratory gases and gas mixtures (calibration gases) and all related equipment for various industries. Sepher gas kavian is active in supplying pure laboratory gases and mixed gases in percent, ppm, ppb such as sulfur dioxide.
Imported sulfur dioxide with 99.9 purity is available in carbon steel cylinders.
Sulfur dioxide gas with a purity of 99.9 is available in a 5-liter cylinder in the amount of 0.75-1 kg.
Sulfur dioxide gas with a purity of 99.9 is available in a 10-liter cylinder in the amount of 0.75-1 kg.
Resources
The main sources of this gas are:
Power plants: Power plants that burn fossil fuels, such as coal and oil, are the largest source of SO2 emissions.
Industrial boilers: Industrial boilers that burn fossil fuels also emit large amounts of SO2.
Metal smelting: The smelting of metal ores, such as copper and zinc, releases SO2 into the air.
Volcanic eruptions: Volcanic eruptions can release large amounts of SO2 into the atmosphere.
Transportation: Vehicles that burn fuel with a high sulfur content, such as diesel fuel, emit SO2 into the air.
Technical specification
| Chemical formula | SO2 |
| Molecular weight | 64.066 g/mol |
| Appearance | Colorless gas with a strong, pungent odor |
| Melting point | -71.3 °C |
| Boiling point | -10.0 °C |
| Density | 2.27 g/L (at STP) |
| Solubility in water | 1.5 g/L (at 20 °C) |
| Vapor pressure | 2.5 mmHg (at 20 °C) |
| Flammability | Non-flammable |
| Toxicity |
Toxic in high concentrations |
Application
(SO2) has a variety of applications in industry and manufacturing. Some of the most common applications include:
Production of sulfuric acid: Sulfur dioxide gas is the main raw material for the production of sulfuric acid, which is a major industrial chemical.
Papermaking: This gas is used in the production of paper to bleach the pulp and to control the pH of the water.
Textile manufacturing: Sulfur dioxide is used in the textile industry to bleach fabrics and to remove unwanted odors.
Fumigation: Sulfur dioxide is used as a fumigant to kill pests in food and other products.
Brewing: This gas is used in brewing to preserve beer and to prevent spoilage.
Disinfectant: Sulfur dioxide is a disinfectant that can be used to kill bacteria and other microorganisms.
Refrigerant: Sulfur dioxide was once used as a refrigerant, but it has been largely replaced by other chemicals due to its environmental impact.
Food preservative: Sulfur dioxide gas is used as a food preservative to prevent the growth of mold and bacteria.
Chemical intermediate: This gas is used as a chemical intermediate in the production of a variety of other chemicals, including sulfites, thiosulfates, and sulfates.

Danger
Respiratory problems: SO2 can irritate the airways and lungs, causing coughing, wheezing, shortness of breath, and difficulty breathing.
Asthma: SO2 can trigger asthma attacks in people who are allergic to it.
Heart disease: Long-term exposure to SO2 can increase the risk of heart disease.
Acid rain: SO2 can contribute to acid rain, which can damage trees, crops, and other plants, and corrode buildings and other structures.
The following are some of the symptoms of exposure to this gas:
Coughing
Wheezing
Shortness of breath
Difficulty breathing
Burning sensation in the eyes, nose, and throat
Watery eyes
Runny nose
Chest tightness
Nausea
Vomiting
Headache
Fatigue
If you are exposed to sulfur dioxide gas, it is important to seek medical attention immediately. Symptoms of exposure may not appear immediately, so it is important to seek medical attention even if you do not feel sick.