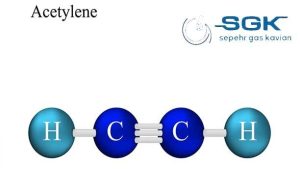
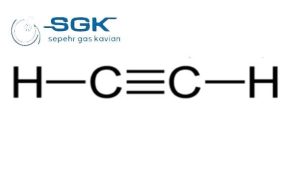
Acetylene gas
Acetylene gas is a colorless, flammable gas with the chemical formula C2H2. It is the simplest alkyne and is the hottest and most efficient of all fuel gases. This gas is unstable in its pure form and is usually handled as a solution in acetone or DMF.
Sepher gas kavian company is the reference laboratory of the standard department in the field of producing and importing laboratory gases for various industries and laboratory equipment and quantum measurement devices and gas mixtures (calibration gases) with high quality and all equipment related to various industries.
The company’s activity in the field of C2H2 is as follows:
- Laboratory acetylene gas cylinder with purity of 99.5 and 99.8 grade 2.5 and 2.8
- Acetylene gas cylinder for laboratory use, welding and cutting, atomic absorption device
- Charging pure acetylene capsule with 18 bar pressure
The volume of cylinders and capsules available for charging acetylene gas is: 7 pin, 12 pin, 40 liter
- DIN1, BS4 acetylene gas cylinder valve

Resources
There are three main sources of this gas:
Calcium carbide: Calcium carbide is a solid compound that reacts with water to produce this gas. This is the most common method for producing this gas on a commercial scale.
Steam cracking of ethylene: Ethylene is a gas that is produced from the cracking of hydrocarbons. When ethylene is steam cracked, it produces acetylene gas as a byproduct.
This gas is also found in small amounts in the atmosphere, but it is not a significant source of the gas.
Here are some additional details about each of these sources of this gas:
Calcium carbide: Calcium carbide is produced by reacting lime and coke in a blast furnace. The calcium carbide is then reacted with water to produce this gas. This reaction is exothermic, meaning that it releases heat. The heat must be removed to prevent the C2H2 from exploding.
Partial combustion of methane: Methane is a gas that is found in natural gas and petroleum. When methane is partially combusted, it produces acetylene gas as a byproduct. The partial combustion of methane is a relatively inefficient process, but it is a cost-effective way to produce acetylene gas.
Steam cracking of ethylene: Ethylene is a gas that is produced from the cracking of hydrocarbons. When ethylene is steam cracked, it produces this gas as a byproduct. The steam cracking of ethylene is a more efficient process than the partial combustion of methane, but it is also more expensive.
Technical specification
| Chemical formula | C2H2 |
| Molecular weight | 26.04 g/mol |
| Color | Colorless |
| Odor | Garlic-like |
| Density | 1.11 kg/m3 (at 20°C and 1 atm) |
| Boiling point | -84.7°C |
| Melting point | -80.75°C |
| Flammability limits | 2.5% to 83% in air |
Application
C2H2 is a versatile gas with a wide range of applications. It is used in welding, cutting, chemical synthesis, glassmaking, and brazing.
Welding and cutting: This gas is a popular fuel for welding and cutting metals. It produces a very hot flame that is ideal for these applications. C2H2 is used in oxy-fuel cutting, which is a process that uses a mixture of this gas and oxygen to cut through metal.
Chemical synthesis: This gas is a versatile chemical building block and is used to synthesize a wide variety of chemicals, including acetic acid, vinyl chloride, and acrylonitrile. Acetylene is used in the production of many plastics, fibers, and rubbers.
Glassmaking: This gas is used in the glassmaking industry to heat glass to high temperatures. It is also used to produce borosilicate glass, which is a type of glass that is resistant to heat and chemicals.
Brazing and soldering: C2H2 is used in brazing and soldering to melt and join metal parts. Brazing is a process that uses a filler metal to join two pieces of metal together. Soldering is a process that uses a molten solder to join two pieces of metal together.
Danger
Here are some of the dangers of this gas:
Fire hazard: This gas is highly flammable and can explode if mixed with air in the wrong proportions. The flammable range of this gas in air is 2.5% to 83%. This means that if the concentration of acetylene in air is below 2.5%, it will not burn. If the concentration of acetylene in air is above 83%, it will not burn. However, if the concentration of this gas in air is between 2.5% and 83%, it will burn and can explode.
Explosion hazard: C2H2 can also explode if it is exposed to high temperatures.
Asphyxia hazard: This gas can displace oxygen in the air, which can lead to asphyxiation. This is because this gas is lighter than air, so it will rise to the top of a room. If there is a leak of C2H2 in a room, the acetylene gas will displace the oxygen in the air, making it difficult to breathe.
Health hazards: This gas can also be harmful to your health if you breathe it in. Short-term exposure to acetylene gas can cause headaches, dizziness, and nausea. Long-term exposure to acetylene gas can cause damage to your lungs.